Top 10 Discoveries of 2015
In the year of 2015, science has made many fascinating advancements. Here’s a list of the top 10 discoveries of 2015.
10. Researchers pinpointed the most lightning-struck spot on Earth
At the American Geophysical Union Fall meeting, new research was presented that shows a particular spot in a Venezuelan lake gets struck by lighting 297 out of 365 days a year, on average. Who says lightning never strikes twice? Lake Maracaibo has entered the Guinness Book of World Records as Earth’s lightning hotspot.
9. NASA discovers first Earth-sized planet orbiting a Sun-like star
Kepler-452b, very similar to Earth, orbits a star very similar to our Sun. Also, Kepler-452b takes about 365 days, like Earth, to orbit its host star. Astronomers like to refer to this Earth-like planet as Earth 2.0 due to its similarities to our home planet.
8. 3D video games have been shown to improve memory formation

Who doesn’t enjoy a good video game? The popular belief is that videogames are bad for people, but past research has proven that videogames aid in hand-eye coordination, reaction time, and attention span, etc. Now, though, it has been proven that 3D video games are actually beneficial to memory formation. A study gave a group of students an object identification memory test before and after a two-week period of time where they had them play a 3D video game each day. The students had a 12 percent score increase after the two weeks. Currently, this study is still relatively small but further research into this idea is yet to come.
7. Ancient Brazilian lake offers large quantity of amphibian fossils
In Brazil, a 278 million-year-old lake holds a large population of amphibian fossils. Scientists have found new species of amphibians that lived approximately 251 million years ago on Gondwana, a supercontinent that included Africa, South America, Australia, Antarctica, the Indian subcontinent, and also the Arabian Peninsula.
6. New calculations by astronomers in Spain and the UK suggest that two unknown planets might exist in our solar system, beyond Pluto’s orbit

New research from the University of Cambridge in England and the Complutense University of Madrid in Spain suggests that there could potentially be two more unknown planets lurking far beyond Pluto in our galaxy. Based on their findings, the observations they have discovered does not match solar system theory. There are two major flaws in their data. One is that it goes against current solar system formation model, the other issue is that their data is based off of a very small sample of extreme trans-Neptunian objects. A trans-Neptunian object is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average than Neptune. The idea that there could potentially be more planets in our galaxy is a very exciting thing, but sadly, they have not been discovered quite yet. It’s nice to know the wheels are in motion though.
5. Scientists discover the “consciousness switch” responsible for awareness
A research team deriving from Stanford University is believed to have found the part of our brain that controls human awareness. The path to this has ended in a multitude of failures due to not having the proper techniques to activate or deactivate consciousness. Two cases have been recorded over the past eight years are the only successes. Researches believe that a region of the brain called the thalamus could be responsible for consciousness. The team conducted studies by stimulating the neurons of the thalamus of rats. They found that stimulating the rat’s thalamic neurons at a rate of 10 times per second caused the rats to lose consciousness, while stimulating it between 40 to 100 times per second woke up the rats. The head researcher on this project believes that this treatment could potentially help patients with traumatic brain injuries in the future.
4. DNA startup company called Cambrian Genomics revolutionizes editing and creating DNA
In San Francisco, a DNA startup company called Cambrian Genomics, raised $10 million to create and edit DNA for major pharmaceutical companies. So far on the market this company has: color-changing flowers, cow-free milk, animal-free meat, tests that detect diseases from one drop of blood and pills that tell doctors whether you have taken your medicine. The company’s goal is to create new creations with minimal restrictions. This could advance technology in ways that are unimaginable in this day and age, with further research of course.
3. Researchers grow human skeletal muscle in the laboratory that reacts to stimuli as normal skeletal tissue does
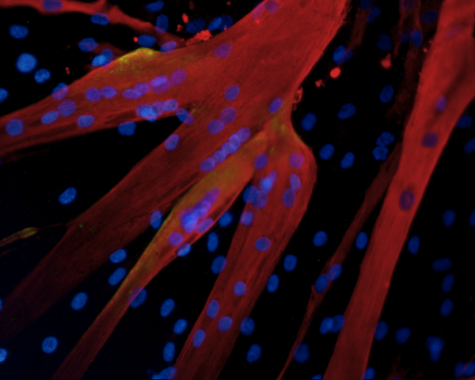
Researchers have grown skeletal muscle that reacts to stimuli just like human skeletal muscle does. This could potentially serve as a “test bed” for clinical trials. The skeletal muscle reacts to a myriad of different drugs and is hoped to soon replace animals in clinical trials.
2. A new physics model shows that the universe might have existed forever
In 1915, Einstein published his theory of general relativity. The theory of general relativity predicts that the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old. Many scientists believe the universe was in a dense and singular point and did not truly begin until there was a Big Bang to expand it. Many believe the issue with the Big Bang is that mathematics can only show what happened after it, not before or doing the actual event. Researchers from University of Lethbridge in Alberta, Canada have developed a quantum equation that they believe can prove that the universe may in fact have existed forever, with no beginning.
1. Scientists create the first map of the human epigenome
An epigenome is defined as, “a network of chemical compounds surrounding DNA that modify the genome without altering the DNA sequences and have a role in determining which genes are active in a particular cell.” Now, keeping this in mind, using massive data analysis, scientists have been able to put together the largest and quite frankly the first map of the human epigenome. They have used this to try and understand why and really how certain genes can turn themselves on and off in human cells. Some people may remember the Human Genome Project, which paved the road and provided with a complete map of the genes that map up our DNA. While the map of genes is very important and was used heavily in the creation of the epigenome map, genes are merely players and epigenomes are the coaches. Epigenomes run the show. They modify the genome without harming the DNA and they are the ones who can turn on and off the genes in certain cells. This research is aiding the finding of mutations linked to different diseases, such as Alzheimer’s.